Are you ready to discover the secrets of living soil? Get ready to delve into a world where plants thrive in a natural environment packed with beneficial microorganisms.
After reading this blog post, you'll have a solid understanding of living soil and its components. Also, you'll know how to create your own for healthier, more sustainable cannabis cultivation. Let's get started!
Overview
-
Living soil provides an ideal environment for cannabis plants to reach their fullest potential.
-
It's composed of organic matter, minerals, water, air, and microorganisms that work together in a soil food web to create a healthy ecosystem.
-
Microorganisms (bacteria, nematodes, fungi, insects, and earthworms) break down organic matter into nutrients that cannabis plants later absorb.
-
Living soil offers higher yields with sustainable growth compared to traditional potting soils or synthetic nutrients.
If you prefer visual content check out our YouTube channel here.
Understanding Living Soil

Living soil is a game-changer in the world of cannabis cultivation. According to the University of Minnesota Extension, it's a natural growing medium teeming with microorganisms that work together to break down organic matter, providing plants with the nutrition they need.
Improved nutrient absorption also results in healthier plants, reduced watering needs, limited erosion, and enhanced aeration.
In other words, living soil mimics outdoor conditions, creating an ideal environment for cannabis plants to thrive.
The Soil Food Web
The soil food web is a complex and fascinating system of interactions between living organisms. It comprises bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and other microorganisms that feed on organic matter, such as decaying plants, animals, and microbes, as well as nutrients released by living plant roots.
This intricate web plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem, protecting plants from pests and diseases. It also shields them from drought and flooding.
To ensure a healthy soil food web, it's vital to add compost and other types of organic matter and introduce beneficial organisms, such as earthworms.
Soil Microbes and Their Functions
Soil microbes, the unseen majority in the soil ecosystem, are tiny living organisms. As mentioned, they include fungi, bacteria, archaea, protozoa, and viruses.
These microorganisms have a significant impact on soil health and plant growth. Soil microbes release enzymes that transform complex molecules into simpler ones. Therefore, they play a crucial role in nutrient cycling.
After decomposing organic matter, excess nutrients are released back into the soil in forms that plants can absorb and use.
Additionally, soil microbes enhance soil structure by increasing organic matter content, which improves the ecosystem's ability to retain water and nutrients. They also create a more porous soil structure, allowing better air and water flow.
Components of Living Soil

Essentially, living soil is a unique blend of organic matter, minerals, water, air, and microorganisms. You already know what the soil microbes category includes, but what about the organic components?
The organic matter used in living soil often includes peat, compost, coco coir, manure, and worm castings. These components improve the soil's ability to supply essential nutrients and break down minerals.
Plus, organic matter gives the soil all the necessary nutrients for microbial activity. As a result, the ecosystem's microorganisms release compounds that bind soil particles, favoring aggregate stability, water infiltration, and water holding capacity.
Besides coco coir, compost, and other types of organic matter, specialist companies even add rock dust, dolomite lime, and custom ingredients, such as ground beetle shells and powdered crustacean shells, to ensure plants receive sufficient calcium and magnesium.
Beneficial Organisms
Beneficial organisms are the life force of living soil, working together to create a thriving ecosystem for plant growth. Besides bacteria, fungi, mycorrhizae, and protozoa, these organisms may include algae and larger creatures, such as earthworms, pillbugs, and some nematodes. They help cycle nutrients, break down crop residues, and stimulate plant growth, preventing nutrient leaching and diseases.
To ensure a healthy population of beneficial organisms, growers may introduce amendments and organic inputs, such as wood ash, green manure, and kelp meal into the soil.
Kelp meal, for instance, brings nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, zinc, manganese, iron, sulfur, copper, and magnesium to the soil, promoting a healthy and diverse ecosystem.
Organic Matter Sources
Organic matter sources form the backbone of living soil. They include living and dead plants, animal remains, compost, manure, cover crops, and leaf litter.
There are two types of organic matter sources:
- Living organic matter sources: They include living plants, animal remains, and cover crops.
- Dead organic matter sources: They consist of dead plants, compost, manure, and leaf litter.
By incorporating a diverse range of organic matter sources, living soil becomes a rich, fertile, and sustainable growing medium for cannabis plants.
Creating Your Own Living Soil for Cannabis Cultivation

Creating your own living soil for cannabis cultivation involves a three-step process: building a base, amending the soil, and "cooking" the soil.
By building a strong base, amending it with the right nutrients, and allowing the soil to "cook," you set the stage for microbes to feed on organic matter and create living soil that's ready for cannabis.
The result is a healthier, more sustainable, and cost-effective way to grow cannabis.
Building a Base
A strong base for living soil is essential, as it supports plant growth. However, there are other advantages. It allows growers to reuse the soil for a long time, saving money on labor, fertilizer, and growing media, for example.
Base building involves a variety of components. Popular choices include peat, compost, coco coir, manure, worm castings, and perlite. Each one has its own unique benefits.
Overall, each of these materials contributes to the foundation of an entire ecosystem, enabling cannabis plants to grow and thrive in a nutrient-rich environment.
Amending the Soil
Amending the soil is another crucial step in creating living soil for cannabis cultivation. The Colorado State University Extension explains that adding organic matter sources, such as compost, manure, and mulch, enhances soil properties and reduces the risk of harmful plant diseases.
Amendments also play a vital role in improving water retention and creating a better environment for plants to grow.
By introducing beneficial organisms through amendments, the soil ecosystem is strengthened, and plants can access the nutrients they need for healthy growth.
"Cooking" the Soil
The term "cooking" the soil refers to the process of allowing the soil to rest and settle for a while before planting. This crucial step helps the microbes in the soil to start breaking down the amendments and transforming them into forms that plants can use.
Ideally, the soil should "cook" for at least two weeks but up to a month is best. During this time, it's important to keep the soil moist and aerated, so the microbes can do their job.
Growing Cannabis in Living Soil: Tips and Techniques
To make the most of your living soil, it's essential to ensure healthy plant starts and optimize environmental conditions.
By doing so, you'll provide your cannabis plants with the best possible environment for growth and development, enabling them to flourish and produce higher yields.
In this regard, here are a few tips and techniques for growing cannabis:
Ensuring Healthy Plant Starts
Healthy plant starts are crucial for successful cannabis cultivation in living soil. Starting with a clone from a thriving mother plant or germinating seeds ensures that your plants begin their life cycle strong and healthy.
If a pest problem arises, you can add diatomaceous earth to the living soil as a natural pesticide. By focusing on healthy plant starts, you set the stage for robust and productive cannabis plants.
Optimizing Environmental Conditions
You should optimize environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light, to achieve the best results when growing cannabis in living soil.
Maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem is also vital, as doing so will keep the soil food web balanced and functioning properly.
GROWHub, an environmental monitoring software, can be a valuable tool in this process, as it offers a complete overview of your cultivation facility's conditions and records over time for analysis.
Comparing Living Soil to Other Growing Methods
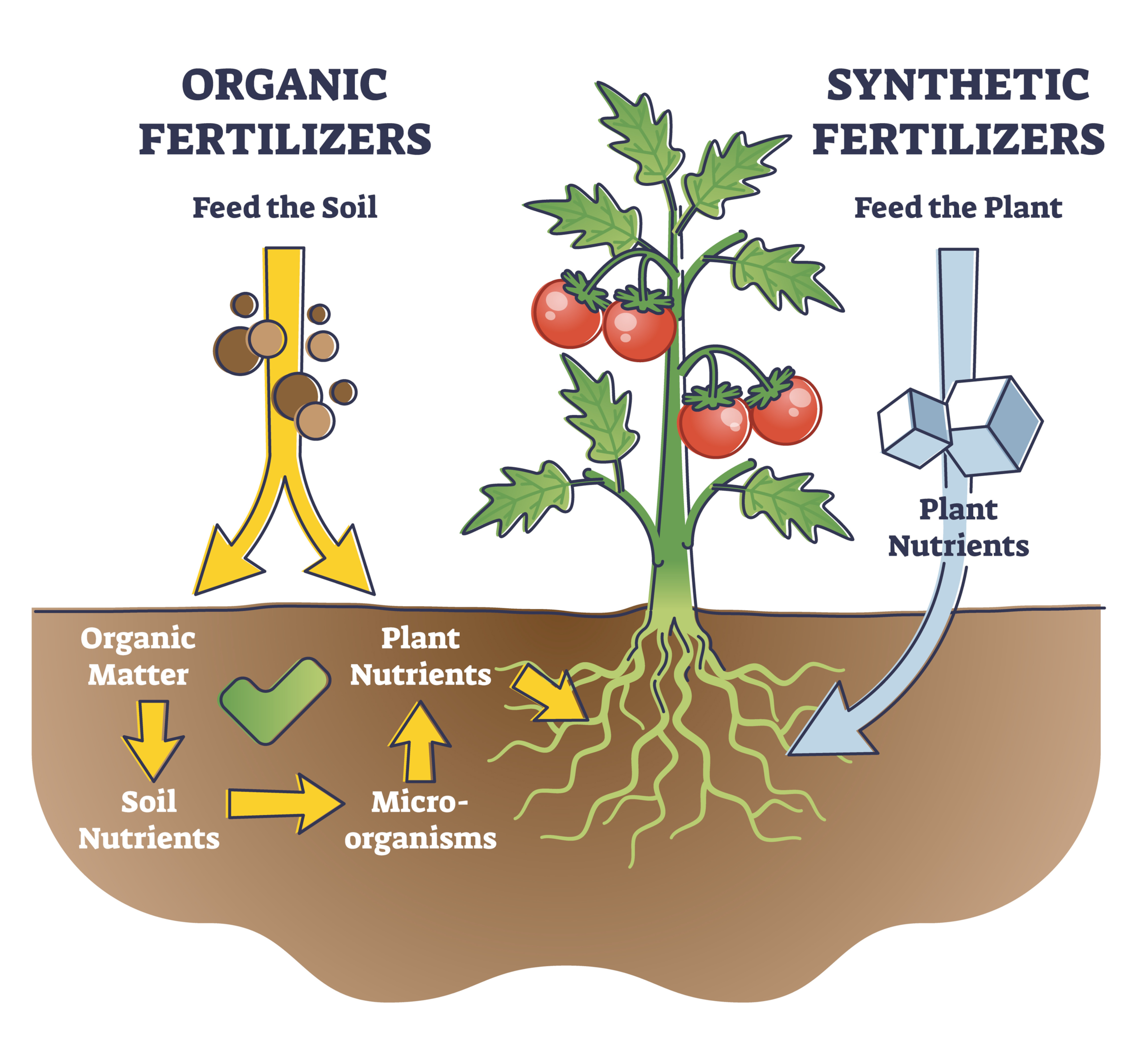
When comparing living soil to other growing methods, it becomes clear that organic nutrients are preferred over synthetic ones, and living soil is far superior to standard potting soil.
Organic nutrients feed the microorganisms in the soil, promoting a healthy soil ecosystem, while synthetic nutrients feed the plant directly, potentially causing nutrient imbalances.
As more growers recognize the benefits of living soil, its popularity and usage continue to grow.
Organic vs. Synthetic Nutrients
Organic nutrients, which are derived from natural sources, such as plants and animals, offer numerous advantages over synthetic nutrients, which are inorganic compounds created by humans.
While organic nutrients help to boost soil structure and fertility, synthetic nutrients provide a quick supply of the nutrients plants need.
However, synthetic nutrients can be more difficult to manage and may cause nutrient imbalances in the soil, potentially affecting plant health.
Living Soil vs. Standard Potting Soil
Living soil offers many benefits over standard potting soil. It contains live microbes that boost plant growth and is made from sustainable, natural ingredients.
On the other hand, standard potting soil is typically sterilized and lacks the diverse microorganisms and nutrient content found in living soil.
By choosing living soil over standard potting soil, you provide your cannabis plants with a nutrient-rich and supportive environment for growth and productivity.
The Future of Living Soil in Cannabis Cultivation

The future of living soil in cannabis cultivation looks brighter than ever. As more growers recognize the benefits of this natural growing method, they're increasingly adopting it to grow high-quality, sustainable cannabis.
Additionally, the use of living soil simplifies the cultivation process by reducing the need for bottled nutrients. When properly conditioned, the soil can be reused multiple times, saving money and resources.
As the cannabis industry continues to evolve, the prominence of living soil is expected to grow, leading to healthier plants and a more sustainable approach to cultivation.
Summary
To sum up, living soil is a game-changer for cannabis cultivation. With its unique blend of organic matter, beneficial organisms, and optimal environmental conditions, living soil provides a natural and sustainable method for growing healthy cannabis plants.
By understanding the components of living soil, creating your own, and following key tips and techniques, you can unlock the full potential of this incredible growing medium. It's time to embrace living soil and revolutionize how you cultivate cannabis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What makes the soil a living soil?
A: Living soil is alive with millions of beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, worms, and microarthropods. These critters interact to break down organic matter into elements that plants can use to create energy, grow roots and produce vibrant leaves and fruits.
They also create a protective barrier against pests, disease, and drought, helping you grow healthier plants.
Q: How do you make living soil?
A: Making living soil is relatively straightforward - just combine sphagnum peat moss, aeration, and high-quality compost or earthworm castings in the right proportions. This mix will ensure that your organic soil is rich in essential nutrients and healthy microbes.
With a little effort, you can create the perfect environment for your plants to thrive!
Q: Is living soil the same as potting soil?
A: No, living soil and potting soil aren't the same. Living soil is minimally processed and contains live microbes that help promote plant growth. Contrastingly, potting soils have been sterilized and don't contain such beneficial components.
Q: What are the pros and cons of living soil?
A: Living soil offers gardeners the opportunity to achieve full organic growth without the use of bottled additives, but there is a risk of unwanted bacteria, fungi, and other pests.
Additionally, living soil may need more frequent flushing than traditional soil setups.
Ultimately, the decision to use living soil should be weighed against your garden's unique needs.
Q: What is the best blend of ingredients to make living soil?
A: To make living soil, start with a balanced mix of sphagnum peat moss, perlite, and compost. Aim for a 50/30/20 ratio.








